M.S. research
A detailed description of my M.S. research can be found in the M.S. Research page. The page consists of links to the manuscript and code repository, descriptive graphics, interactive point cloud viewers, and a short video presentation. Click here to navigate to the M.S. Research page.Collaborative research:
"A comparison and development of methods for estimating sagebrush shrub volume."
Role: Collaborative Researcher, UAV-based rangeland project
Principle investigator: Dr. Georgia Harrison, Department of Plant Sciences, University of Idaho
Faculty advisor: Dr. Jason Karl, Department of Forestry, Rangeland, and Fire Sciences, University of Idaho, Moscow, ID
Project description and funding:
- Examine the suitability of using structure-from-motion derived point cloud generated from drone-captured images to estimate canopy volume.
- Test two frameworks to estimate shrub canopy volume from point cloud: volumetric technique using the 2.5D tool from CloudCompare and allometric techniques replicating field-based measurement methods (see figure and interactive window below).
- Preliminary exploration of the potential application of segmentation algorithms, intially developed for tree-top detection and segmentation, on shrubs.
- This project was funded by the Joint Fire Science Program's Graduate Research and Innovation (GRIN) Fellowship secured by PI Georgia Harrison and is a part of her PhD dissertation.
Interactive examples:
1. Allometric measurement of shrub canopy volume:
Shrub maximum height (a) and two measures of canopywidth (b). H is shrub height, D1 is the longest canopy width, and D2 is the greatest canopy width perpendicular to D1. Volume = ¼ × π × H × D₁ × D₂
Scene > Objects > Measurements" or "Scene > Objects > Annotations" to toggle the visibility of the measurements and annotations respectively.2. Shrub detection and segmentation:
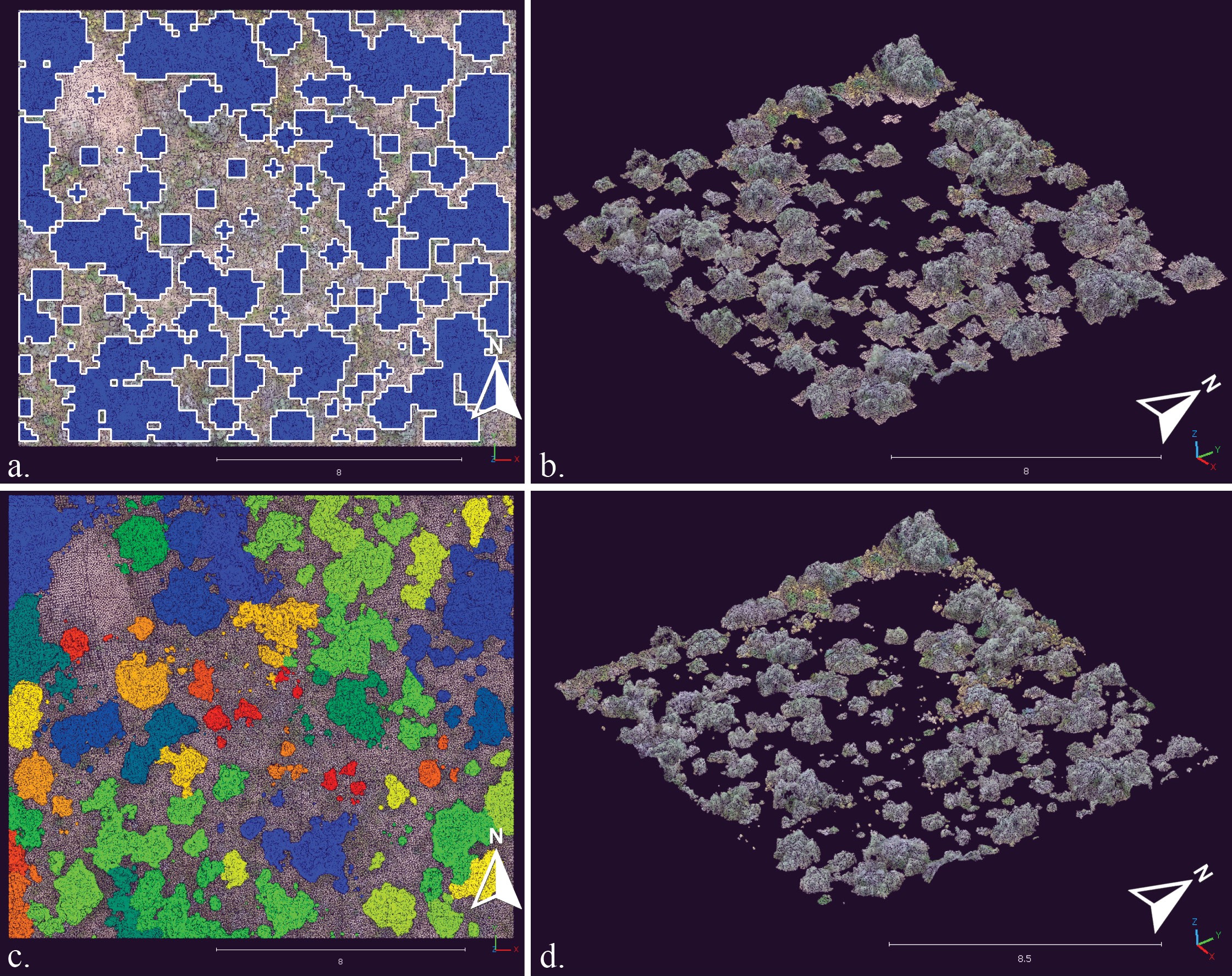
(a) Shrub crown delineations on a subset of the study site (16.2 × 14.2 m) using the variable window filter algorithm outlined as blue polygons are used to clip the point cloud of the study area into (b) individual shrub point clouds. (c) Direct point-cloud segmentation of individual shrubs on the same subset of the study site (16.2 × 14.2 m) represented by a set of repeating colors. (d) Shrubs can be filtered by their ID attribute and exported.

Presentation of shrub detection and segmentation workflow at ESA, Portland, 2023. Session: Remote Sensing And Image Analysis, title: "Seeing shrubs from the sky: an exploration of using drone-based methods to estimate shrub canopy volume"
"Using commercial satellite imagery to study insect outbreaks in the US: Outbreak characteristics and evaluation of Landsat-based algorithms."
Role: Graduate Research Assistant, NASA Commercial SmallSat Data Analysis (NASA CSDA) project
Project decription: This is a collaborative research project with researchers from the University of Idaho, Washington State University, and the US Forest Service Rocky Mountain Research Center.
Principle Investigator: Dr. Arjan Meddens, School of the Environment, Washington State University, Pullman, WA
Responsibilities:
- conduct collaborative research to develop machine learning image classification algorithms (RF, MLC, NN) that assess forest mortality using high-resolution satellite imagery
- assist field crew with forest inventory data collection (FIA-based)
- create and maintain spatial databases; perform logistics mapping
- execute drone imagery acquisition missions
Journal article (pre-print): Developing a Rapid Classification Approach for Using Very High-Resolution Satellite Imagery to Map Insect-Caused Forest Disturbances.
🚧 Additional information will be available after the publication of the manuscript! 🚧
Undergraduate Research
GIS-based study of topographical preference of common tree species in Palisades-Kepler State Park, IA (Senior Honors Thesis, Coe College, Cedar Rapids, IA, 2019)Abstract:
The study seeks to develop an understanding of the topographic characteristics that influence tree species composition of upland forests at Palisades-Kepler State Park, Linn County, Iowa. The role of Quercus alba, white oak, is a focus of this study. 123 plots containing 706 trees were sampled with the use of GPS receivers and field methods in the summer of 2017. The sampled field data were combined with its respective GPS data, and mapped on Digital Elevation Model imagery. Geographic Information System (GIS) analyses are used to develop a model of sites suitable for oak regeneration and maintenance within this forest.
- Research blog URL: https://oaksatpalisades.home.blog/
- Thesis info URL: https://coecollege.on.worldcat.org/oclc/1137317800

